- Change theme
What Is an Example of Computer Vision?
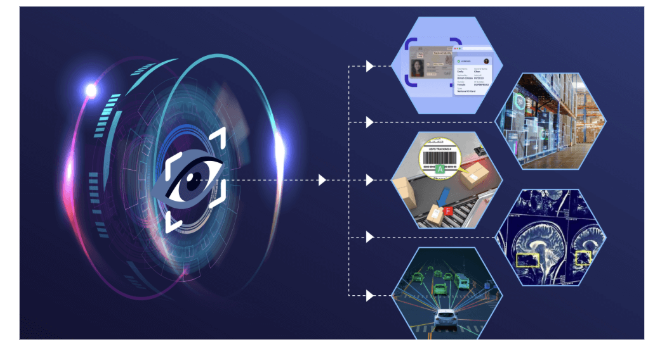
Computer Vision AI, in a sense, is one of the areas of Artificial Intelligence that enables computers to read, process, and interpret visual info.
06:13 08 March 2025
What Is Computer Vision, Fundamentally?
Computer Vision AI, in a sense, is one of the areas of Artificial Intelligence that enables computers to read, process, and interpret visual information. It imitates human eyesight by enabling computers to detect objects, label images, and recognize patterns from videos.
Unlike the traditional rule-based image processing, today's Computer Vision software programming depends on deep learning and neural networks to fetch useful information from video streams and images. Some of these applications are face identification, automated factory defect detection, and self-driving capabilities.
How Does Computer Vision Work at a High Level?
A Computer Vision solution operation executes the following steps:
- Image Acquisition – Taking pictures or video using cameras, sensors, or other devices.
- Preprocessing – Image quality enhancement through correction of brightness, contrast, and noise filtering.
- Feature Extraction – The extraction of meaningful visual features such as edges, shape, and texture.
- Classification and Detection – Use of machine learning algorithms to identify objects, patterns, or anomalies.
- Decision-Making – Where findings are incorporated into an integrated automated, tracking, or real-time decision-making system.
Computer Vision development services can train models to recognize complex patterns with high accuracy by using deep learning and convolutional neural networks (CNNs).
What Are Successful Cases of Computer Vision Solutions?
- Autonomous Vehicles
Computer Vision AI is used most often in autonomous vehicles. Tesla, Waymo, and more use a specific Computer Vision solution to interpret camera data in real-time, LiDAR, and radar in order to identify road signs, pedestrians, and other vehicles. This enables self-driving vehicles to drive safely with no human intervention.
- Medical Imaging & Healthcare
In medical practice, Computer Vision services facilitate disease diagnosis through medical imaging. With AI, CV software can examine X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to identify abnormalities such as tumors, fractures, or brain disorders more accurately than existing processes.
- Manufacturing & Quality Control
Factories use Computer Vision software development services to automate quality inspection by using cameras with AI eyes that scan products to detect flaws and put only quality products on the shelves for sale.
- Facial Recognition & Security
Facial recognition software based on Computer Vision software development is used for security, i.e., airport scanning, mobile login, and surveillance.
- Retail & E-Commerce
Retailers use Computer Vision AI to handle inventory, cashierless shops, and personalized customer service. For example, Amazon Go shops use cameras and AI tools to allow consumers to shop and not check out in a conventional manner.
- Precision Farming & Agriculture
Agricultural growers use Computer Vision systems to monitor plant health, detect parasites, and control irrigation systems. Camera-equipped drones with AI travel over soil types and plant growth in an effort to increase agricultural yields.
What Are the Key Components or Technologies That Enable Computer Vision?
Existing Computer Vision AI app development relies on the following technologies:
- Deep Learning & Neural Networks – AI models such as CNNs and transformers process images with high precision.
- Edge Computing – Local device-based real-time processing reduces latency and enhances performance.
- 3D Imaging & LiDAR – Used for depth perception in autonomous vehicles and robotics.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Integration – Digital overlays enhance real-world interactions.
- IoT & Smart Cameras – Connected devices make it possible to collect masses of data for AI-based analytics.
These technologies underpin Computer Vision development services and allow companies to develop smart and scalable CV solutions.
What Are the Challenges of Computer Vision?
Despite its advancements, Computer Vision AI faces several challenges:
- Data Quality & Bias – Poor image quality or biased data sets can lead to inaccurate predictions.
- High Computational Costs – Training deep learning models requires extensive computational power.
- Complex Environments – Lighting conditions, angles, and object occlusion can impact accuracy.
- Security & Privacy Concerns – Facial recognition and surveillance applications raise ethical and regulatory questions.
- Real-Time Processing Constraints – Real-time processing remains challenging to accomplish on low-power devices.
What Are the Potential Future Applications of Computer Vision?
The future of Computer Vision AI is promising, with emerging applications that can transform industries:
- AI-Powered Smart Cities – Intelligent traffic management, optimized waste management, and enhanced public safety through real-time insights.
- Smart Robotics & Automation – Empowering robots to sense their environment and perform complex tasks autonomously.
- Next-Generation Healthcare – AI-powered imaging for faster, more accurate disease diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Metaverse & Virtual Reality (VR) – Providing simulated, immersive digital experiences driven by AI-driven scene recognition.
- Personalized Retail Experiences – AI-driven virtual shopping assistants and smart fitting rooms.
Conclusions
Computer Vision AI is revolutionizing sectors by enabling machines to interpret and process visual information at the level of human accuracy. From autonomous vehicles to medical diagnosis and retail automation, Computer Vision development services are revolutionizing business across many sectors.
As businesses seek to leverage AI-driven insights, Computer Vision software development will be one of the most significant means of staying ahead in a more automated and data-driven future.
