- Change theme
Medical Pressure Transducer 101: Definition, Functions, and More
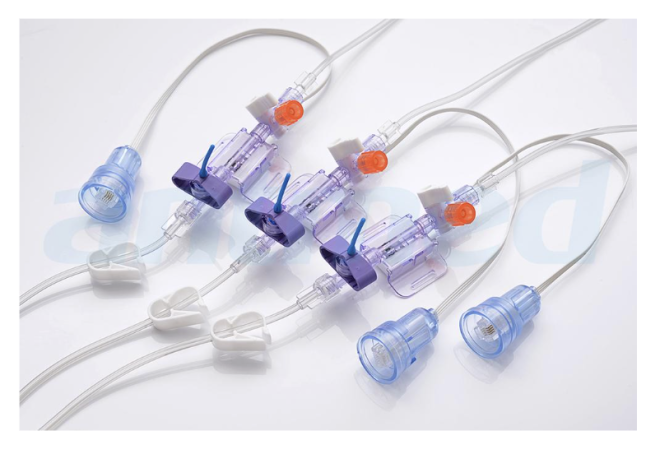
A medical pressure transducer transforms mechanical pressure into an electrical signal for real-time blood pressure monitoring.
03:26 12 November 2024
A medical pressure transducer transforms mechanical pressure into an electrical signal for real-time blood pressure monitoring. It delivers direct arterial or venous pressure measurements for critical care hemodynamic evaluation via catheters or arterial lines.
This article will guide you through the definition, functions, and applications of medical pressure transducers; keep reading to learn more!
What is a Pressure Transducer?
Definition
A medical pressure transducer is a device that converts physiological pressures, including arterial, venous, or intracranial pressures, into electrical signals for monitoring in medical applications. Such pressures must be measured with accuracy for patient safety in critical care scenarios.
The transducer's role is to maintain a consistent electrical output relative to the pressure changes it detects. For instance, in hemodynamic monitoring, the transformation allows clinicians to track a patient's cardiovascular status in real-time. Unconventional versions might be calibrated to work with fluids or gasses in clinical environments for greater fidelity of pressure data.
Types
There are two types of pressure transducers: disposable and reusable. Disposable transducers are used in single-use settings in intensive care to prevent contamination and guarantee sterility. They are pre-calibrated for short-term use. In contrast, reusable transducers are built for durability and cost-effectiveness over multiple uses but need regular recalibration and sterilization.
Beyond such categories, there are fiber-optic transducers. They are more resistant to electromagnetic interference and benefit environments with high electrical noise. Piezoelectric-based models, which detect pressure via voltage change across crystals, are another example of transducer types.
How They Work
The working principle of a pressure transducer converts mechanical pressure into an electrical signal that can be interpreted by various devices. A pressure transducer generally comprises a sensing component that is subjected to the pressure being assessed, along with an electronic circuit that converts the changes in pressure into a voltage signal.
Most transducers use a strain gauge with a diaphragm; when pressure is applied, the diaphragm deforms and alters the electrical resistance of the strain gauge into an electrical output.
Functions and Applications
Core Functions of Medical Pressure Transducers
Medical pressure transducers directly monitor physiological pressures. For example, in arterial blood pressure monitoring, the transducer enables precise, real-time measurement of systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial pressures. Furthermore, in respiratory monitoring, they detect minute variations in airway pressures during mechanical ventilation. The signals help clinicians adjust ventilator settings for oxygenation.
Meanwhile, pressure transducers are used in intracranial pressure monitoring to measure subtle changes within the brain's compartments to detect dangerous shifts or increases. The high sensitivity and accuracy of such devices help monitor critical patients.
Applications in Medical Settings
Pressure transducers are indispensable in high-acuity ICUs, operating rooms, and catheterization labs. In ICUs, they monitor hemodynamics in patients with cardiac or respiratory instability for real-time data for rapid interventions. In operating rooms, they are integrated into anesthesia machines to manage airway and vascular pressures during surgeries.
For example, intraoperative blood pressure monitoring with transducers guarantees tight control during induction and emergence. In catheterization labs, pressure transducers provide data during coronary interventions while measuring pressures across stenotic lesions.
Real-Time Contribution to Patient Monitoring
Pressure transducers prompt real-time monitoring, so clinicians can observe and react to fluctuations in a patient's condition. For example, in continuous arterial pressure monitoring, transducers allow real-time trend analysis of cardiac output. It gives early warning signs of deteriorating cardiac function. Likewise, they are key to respiratory monitoring since they track airway pressures with millisecond precision so the ventilator delivers the correct tidal volumes and pressure settings.
With real-time, waveform-based data visualization, pressure transducers allow immediate therapy adjustment to avoid barotrauma or hypotension. Their integration into patient monitoring systems confirms that clinicians can respond to physiological changes within seconds.
Antmed's Disposable Pressure Transducers
In critical care and invasive operations, Antmed’s disposable pressure transducers are of high-precision, real-time monitoring, available in single, dual, and triple channel configurations, are designed to ensure precise pressure readings.
Also, Antmed offers Disposable Pressure Transducers with Blood Sampling, which is a needle-free, closed, rapid in-line blood sampling and pressure monitoring system. The negative pressure suction device and self-flush after blood sampling enhance clinical work efficiency; the needle-free connector, as well as high precision flow control, ensures safety and durability. What’s more, the one-handed operation makes it user-friendly.
Conclusion
As an experienced medical disposable supplier, Antmed innovates while controlling the whole production cycle, from R&D to manufacturing. Their postdoctoral R&D stations and Guangdong High-Pressure Imaging Technology Center improve pressure transducer accuracy. Antmed leads specialized medical device development with over 200 patents. If you are looking for top-notch medical pressure transducers, do not hesitate to visit Antmed’s website!
